AI assistants are now integrated into most modern development environments. However, SQL support is still challenging for most engines. Different databases use varied dialects, and there isn’t enough data to train models properly for every variation. PostgreSQL and MySQL don’t handle string concatenation the same way, and Oracle’s date functions don’t match those in SQL Server. These inconsistencies make it difficult for general-purpose AI tools to generate accurate queries across different databases. In this article, you’ll learn how DBeaver’s AI features help you write SQL faster, troubleshoot errors, and work with unfamiliar code.

DBeaver’s AI features work around these limitations by combining AI with your actual database context, helping you translate natural language to SQL and troubleshoot queries without manually adapting to each dialect.
What makes AI for SQL in DBeaver different from ChatGPT
When you use ChatGPT or another external AI chatbot to create a database query, you have to provide all the context yourself: database type, table names, column names, data types, and relationships between objects. Without this metadata, even the best AI model will produce queries that don’t match your schema and will need manual fixes before they run.
Here’s what providing that context by yourself might look like:
Prompt in ChatGPT: “I need an SQL query for an SQLite database that retrieves the first names, last names, emails, and phone numbers of customers, along with the total amount of their invoices. The database has two tables: Customer and Invoice. The Customer table includes columns CustomerId, FirstName, LastName, Email, and Phone. The Invoice table includes columns CustomerId and Total. Please use a LEFT JOIN to ensure all customers are included, even if they have no invoices, and group the results by customer details.”

But, in DBeaver, the prompt will look like this: “Show customers’ names, last names, emails, phones, and add their invoice totals”.
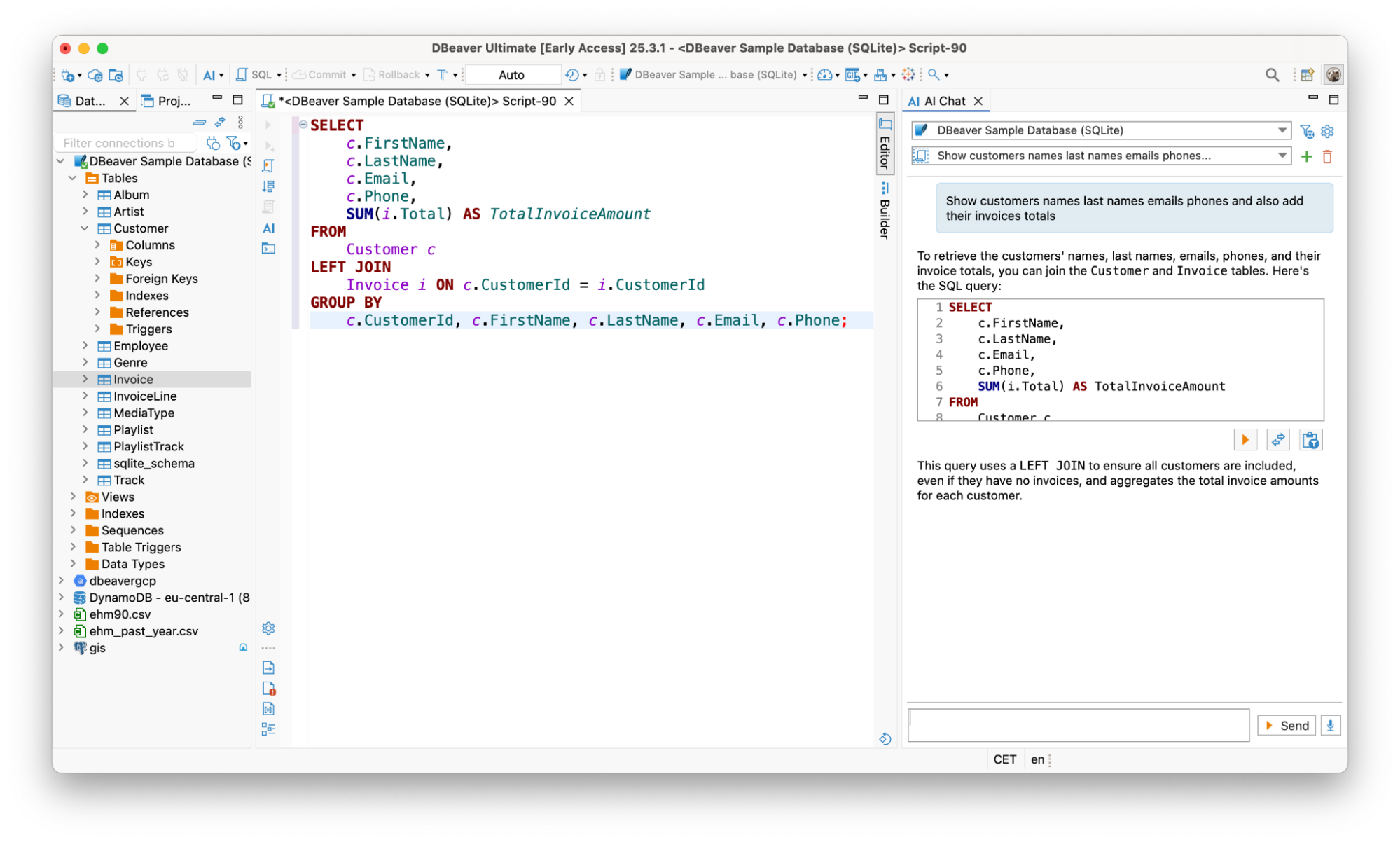
That’s what makes DBeaver different. It automatically sends your database metadata to the AI engine, so you can describe what data you want to retrieve rather than explaining your entire schema. The AI already knows your tables, columns, data types, and relationships.
One-time requests: a quick way to generate SQL
The quickest way to generate SQL with AI in DBeaver is with a one-time request. Simply submit your request, and AI generates a query. Each request is standalone, with no prompt history carried over. While you can’t refine the same request through follow-up prompts, you can use the result as a starting point. Either submit a new request or edit the query manually.
One-time requests work well when you need a simple query quickly, or when you want AI to handle the initial draft while you fine-tune the details yourself. There are two ways to get started:
1. AI Assistant pop-up
When you open the AI Assistant pop-up, you can type requests like “show all orders placed in the past week” or “top 5 customers by revenue,” and it generates the corresponding SQL. The query appears in your SQL Editor, ready to run.
This feature is available only in DBeaver Community as a simple way to get started with AI. DBeaver PRO products offer more advanced AI tools.
AI Command
You can also generate queries directly in your SQL Editor using AI Command. Type @ai followed by your request (for example, @ai show monthly revenue by product category for the last quarter) and the query appears right in your SQL Editor. This is useful when you’re already working in the editor and want to generate a query without switching context.
AI Command is available in all DBeaver desktop editions, including Community, CloudBeaver PRO products, and both desktop and web versions of Team Edition.
Refine AI SQL queries through conversation with a chat mode
One-time requests are helpful, but they only handle the initial query generation. For more complex tasks, you can use AI Chat in DBeaver PRO, an advanced way to communicate with AI.
Like AI Command and AI Assistant, AI Chat handles your database context automatically. The key difference is that you can refine your query in real time through conversation. You start with a basic request like “show total sales by region,” then add follow-up prompts like “add a filter for November invoices” or “group results by customer region.”
Each time, the AI generates an updated query based on your conversation. When the query meets your needs, you can run it or copy it directly to the SQL Editor.
With this approach, AI becomes not only a query generator, but also a query analyzer and optimizer. You can build complex queries step-by-step without writing a single line of SQL code yourself.
If you prefer hands-free work, you can also use speech recognition to speak your prompts instead of typing. This feature currently works with Whisper 1, GPT-4o mini Transcribe, and Gemini 2.5 Flash.
Explain and fix queries with AI
You can use AI in DBeaver for more than generating new queries. It also helps you understand and fix existing SQL.
When you’re reviewing unfamiliar or legacy code, select a query and ask AI to explain what it does in plain language. This is especially useful when working with complex logic or inherited projects.
You can also fix broken queries on the fly. When a query fails, press the Explain and Fix button to identify the problem and apply a suggested correction immediately. If you’ve forgotten to close a parenthesis or used the wrong join syntax, the AI will detect it and offer a fix. This saves time spent debugging and helps you learn from mistakes as you go.
These features are available in DBeaver PRO products.
Get AI suggestions while writing SQL
If you prefer writing queries manually, you can still get help from AI directly in the SQL Editor. Right-click or use a keyboard shortcut to call AI SQL Query Suggestion. You’ll see ghost-text suggestions based on your current code that you can accept to complete your statements.
AI suggestions are based on your database metadata and the queries you’ve already written in the editor. AI Query Suggestion can assist you at any step of query creation and covers different types of SQL statements, including SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and more.
This feature is available in DBeaver PRO desktop products. AI Query Suggestion is currently not available in CloudBeaver Enterprise and Team Edition Web.
AI privacy and data control
With any AI tool, data privacy matters. You control whether DBeaver shares only metadata or includes small data samples when you need more precise results. You can also choose between cloud-based AI providers or local models that never send information outside your network.
By default, only metadata (table names, column names, data types) is used to generate context-aware results. Sharing specific data samples can help AI understand your actual data patterns and generate queries that better match your needs. You can adjust these settings anytime in Preferences > General > AI > AI Configuration.
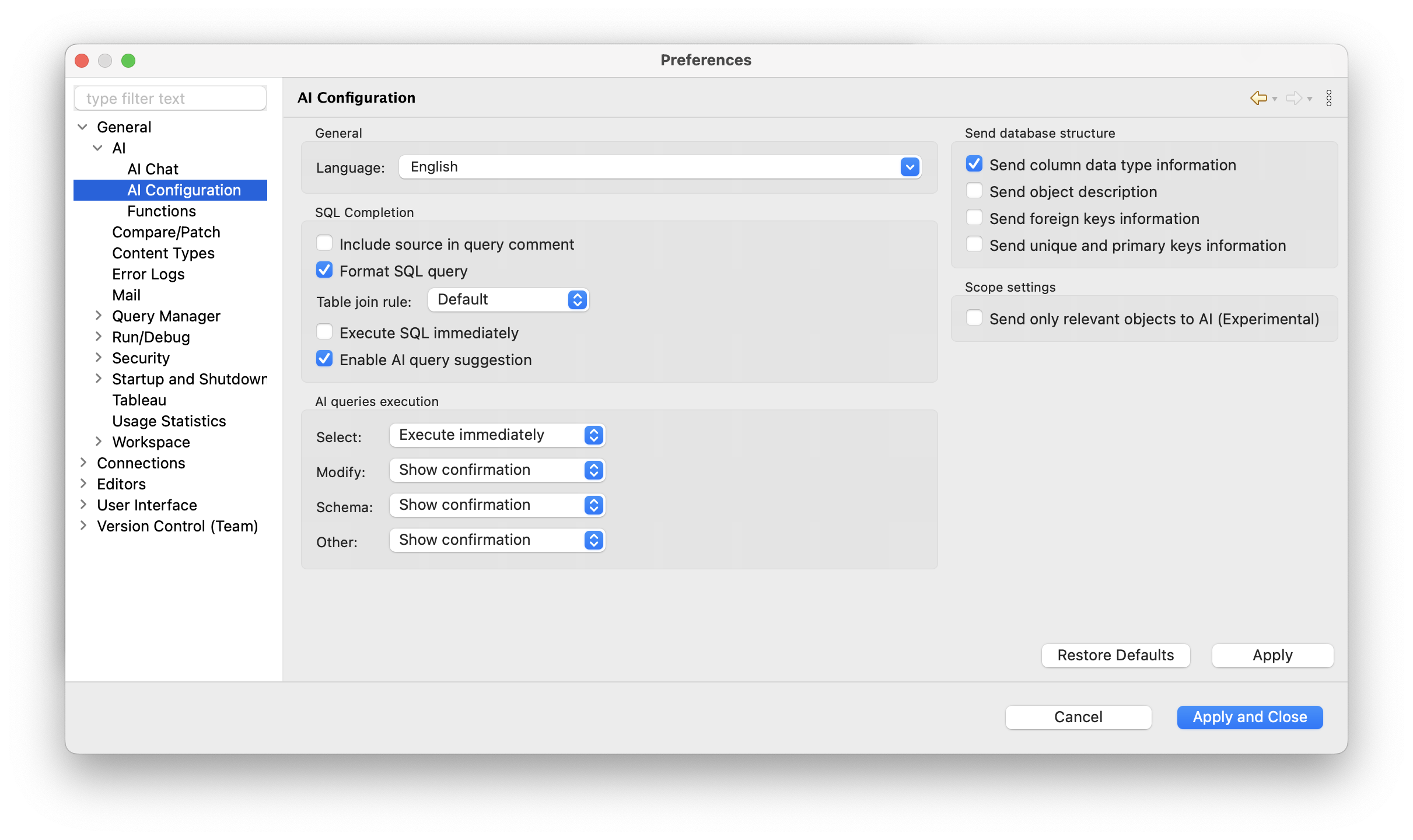
If you prefer to keep everything offline, you can connect DBeaver PRO to local AI models using Ollama. All processing stays within your network, with no data or metadata sent outside. You can set this up in Preferences > General > AI.
Getting started with AI for SQL in DBeaver
The AI features covered here address the most common pain points in SQL development. They’re optional, can be turned on or off at any time, and are designed to reduce manual work while keeping your database metadata secure.
The table below shows which AI features are available in each DBeaver edition:
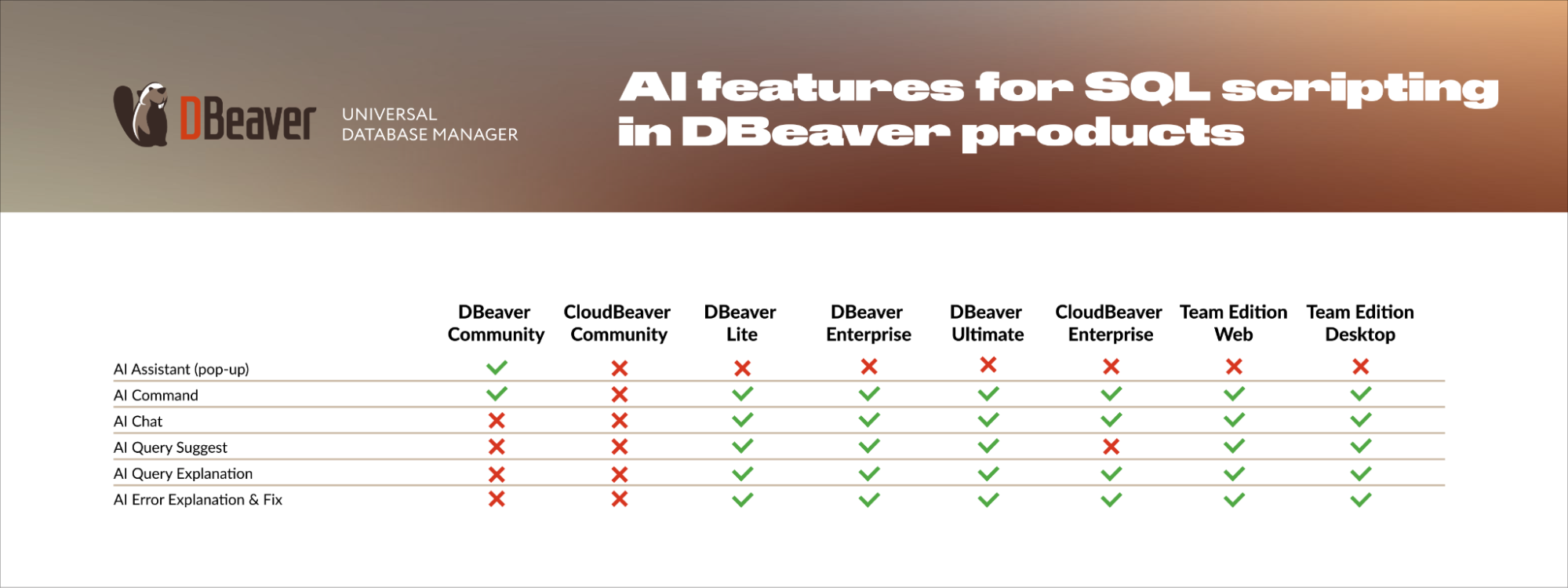
You can use AI Assistant and AI Command in DBeaver Community for free. All DBeaver PRO products offer a 14-day free trial, so you can test the full AI feature set before committing.
We’re here if you need help getting started. Community edition users can open an issue on GitHub, while PRO users can contact the support team.

